RandEquivalent
Description
This operation test is two FSTs are equivalent by randomly generating
N paths alternatively in each of the two FSTs.
For each randomly generated path, the algorithm computes for each
of the two FSTs the sum of the weights of all the successful paths
sharing the same input and output labels as the considered randomly
generated path and checks that these two values are within
'delta'.
The random generation can be specified in the same as for the
RandGen operation.
Usage
template <class Arc>
bool RandEquivalent(const Fst<Arc> &fst1, const Fst<Arc> &fst2,
ssize_t num_paths, float delta = kDelta,
int seed = time(0), int path_length = INT_MAX);
|
template<class Arc, class ArcSelector>
bool RandEquivalent(const Fst<Arc> &fst1, const Fst<Arc> &fst2,
ssize_t num_paths, float delta,
const RandGenOptions<ArcSelector> &opts);
|
fstequivalent --random [-npath=$n] [--delta=$delta] [--seed=$seed] [--max_length=$max_length] in1.fst in2.fst
|
Example
A |
B |
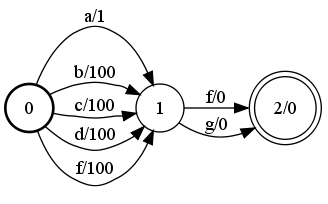 |
 |
RandEquivalent(A, B, npaths, kDelta, RandGenOptions<ArcSelector>());
fstequivalent --random --npath=$npaths a.fst b.fst
ArcSelector |
npaths |
RandEquivalent(A, B) |
UniformArcSelector |
10 |
false |
LogProbArcSelector |
10 |
true |
1000000 |
false |
See Also
Equal,
Equivalent,
Isomorphic